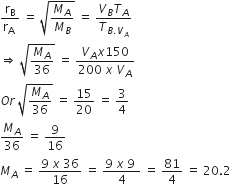20-litre container at 400 K contains CO2(g) at pressure 0.4 atm and an excess of SrO (neglect the volume of solid SrO). The volume of the containers is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container. The maximum volume of the container, when pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value, will be
Given that: SrCO3 ⇌ SrO(s) + CO2(g) kp = 1.6 atm)
-
5 litre
-
10 litre
-
8 litre
-
3 litre
A.
5 litre
Max. the pressure of CO2= Pressure of CO2 at equilibrium
For reaction, SrCO3 ⇌ SrO(s) + CO2(g)
Kp= PCO2 = 1.6 atm = maximum pressure of CO2
Volume Container at this stage,
V= nRT/P .... (i)
Since container is sealed and reaction was not earlier at equilibrium
therefore, n = constant
n= Pv/RT .... (ii)
from equation (i) and (ii) we get
V = (0.4 x 20)/RT = 5 Litre