Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
Sponsor Area
A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements is
-
thick secondary walls
-
pores on lateral walls
-
presence of P-protein
-
enucleate condition
B.
pores on lateral walls
The wall of both vessel and sieve tube elements are perforated by large opening. Due to this adaptation, the cell to cell contact is possible. The vessels are nucleated whereas the sieve tube elements are enucleated.
Sponsor Area
A major characteristic of the monocot root is the presence of
-
Open vascular bundles
-
Scattered vascular bundles
-
Vasculature without cambium
-
Cambium sandwiched between phloem and xylem along the radius
C.
Vasculature without cambium
The characteristic feature of monocot root is presence of vasculature without cambium. The vascular bundles are alternate and radial and arranged in the form of a ring around a central pith. Phloem and xylem bundles are separated by narrow strips called conjunctive tissue and it does not take part in cambium formation. So, the vascular bundles in monocots are closed and do not show any secondary growth.
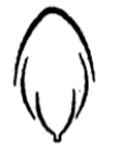
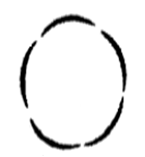
Aestivation of petals in the flower of cotton is correctly shown in
C.

Petals in the flowers of cotton (Gossypium sp) china rose (Hibiscus rosa sinesis), etc, show twisted aestivation. In this type of aestivation, a regular overlapping of petals occurs where one margin of each petal overlaps with the next one petal.
As compared to a dicot root, a monocot root has
-
more abundant secondary xylem
-
many xylem bundles
-
inconspicuous annual rings
-
relatively thicker periderm
B.
many xylem bundles
The vasculature is radial in dicot root i.e.,xylem bundles alternate with phloem bundles. Usually vascular bundles are 2-6 in number while in monocot root the vascular strand consists of several (8 or more) alternate radial xylem and phloem bundles. Secondary growth takes place in dicot root while absent in monocot roots and annual rings do not form.
Black (stem) rust of wheat is caused by
-
Alternaria solani
-
Ustilago nuda
-
Puccinia graminis
-
Xanthomonas oryzae
C.
Puccinia graminis
Black (stem) rust of Wheat is caused by Puccinia graminis tritici, a fungus belonging to Sub-class-Teliomycetidae, Order-Uredinales. It is a heteroecious species which completes its life cycle on two plants, ie, barberry (Berberis) plant and wheat (Triticum aestivum).
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series