A source of sound S emitting waves of frequency 100 Hz and an observer O are located at some distance from each other. The source is moving with a speed of 19.4 ms-1 at an angle of 60o with the source observer is at rest. the apparent frequency observed by the observer (velocity of sound in air 330 ms-1) is 
-
100 Hz
-
103 Hz
-
106 Hz
-
97 Hz
B.
103 Hz
Given, as a source of sound S emitting waves of frequency 100 Hz and an observer O are located at some distance. Such that, source is moving with a speed of 19.4 m/s at angle 60o with source- observer line as shown in figure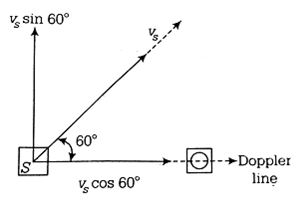
The apparent frequency heard by observer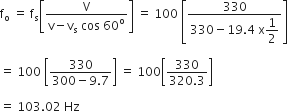






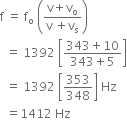



 m/s
m/s



 ...(2)
...(2) is amplitude, k the propagation constant and
is amplitude, k the propagation constant and  the angular frequency,
the angular frequency,
 Speed of transverse wave
Speed of transverse wave 