4.0 g of a gas occupies 22.4 L at NTP. The specific heat capacity of the gas at constant volume is 5.0 JK-1 mol-1. If the speed of sound in this gas at NTP is 952 ms-1, then the heat capacity at constant pressure is.
(Take gas constant R = 8.3 Jk-1 mol-1)
-
8.0 JK-1mol-1
-
7.5 JK-1mol-1
-
7.0 JK-1mol-1
-
8.5 JK-1mol-1
A.
8.0 JK-1mol-1
Given, M = 4 gm
V= 22.4 L,
CV = 5 JK-1 mol-1






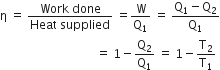
 is the temperature of source and T2 is the temperature of sink
is the temperature of source and T2 is the temperature of sink
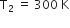

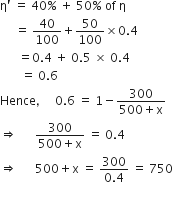

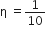 heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the work is done on the system is 10J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
heat engine, is used as a refrigerator. If the work is done on the system is 10J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is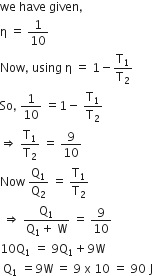
 An isothermal curve is less steeper than the adiabatic curve. So, area under the P-V curve for adiabatic process has more magnitude than the isothermal curve. Hence, work done in adiabatic process will be more than in isothermal process.
An isothermal curve is less steeper than the adiabatic curve. So, area under the P-V curve for adiabatic process has more magnitude than the isothermal curve. Hence, work done in adiabatic process will be more than in isothermal process.
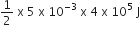 = 1000 J
= 1000 J