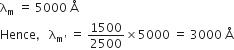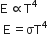A black body at 1227°C emits radiations with maximum intensity at a wavelength of 5000 Å. If the temperature of the body is increased by 1000°C, the maximum intensity will be observed at
-
4000 Å
-
5000 Å
-
6000 Å
-
3000 Å
D.
3000 Å
The product of wavelength corresponding to maximum intensity of radiation and temperature of the body in Kelvin is constant.
According to Wien's law

where  is wavelength corresponding to maximum intensity of radiation and T is temperature of the body in Kelvin.
is wavelength corresponding to maximum intensity of radiation and T is temperature of the body in Kelvin.
Given, T = 1227 + 273 = 1500 K,
T' = 1227 + 1000 + 273 = 2500 K