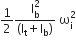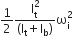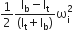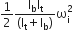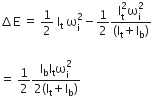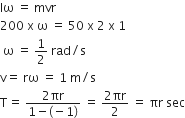The value of α for which angular momentum about origin is conserved is
The value of α for which angular momentum about origin is conserved is
-
-1
-
2
-
zero
-
1
-1
2
zero
1
A.
-1
When the resultant external torque acting on a system is zero, the total angular momentum of a system is zero, the total angular momentum of a system remains constant.This is the principle of the conservation of angular momentum.
Given,






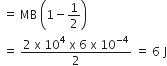
 Another disk of moment of inertia Ib is dropped coaxially onto the rotating disk. Initially, the second disk has zero angular speed. Eventually, both the disks rotate with constant angular speed.
Another disk of moment of inertia Ib is dropped coaxially onto the rotating disk. Initially, the second disk has zero angular speed. Eventually, both the disks rotate with constant angular speed. The energy lost by the initially rotating disc due to friction is
The energy lost by the initially rotating disc due to friction is