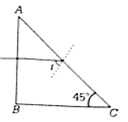
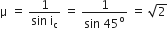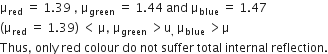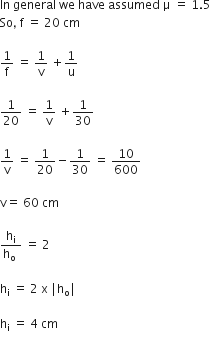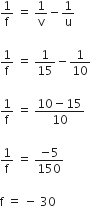A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colours is incident on a right-angled prism. The refractive index of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue wavelength are 1.39, 1.44 nd 1.47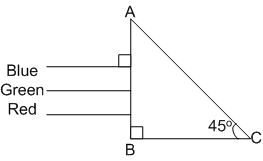
The Prism will
-
separate the blue colour part from the red and green colours
-
separate all the three colours from one another
-
not separate the three colours at all
-
separate the red colour part from the green and blue colours
D.
separate the red colour part from the green and blue colours
For refractive index of a index.