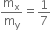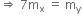B.
BE = [ZMp + (A-Z)Mn -M(A,Z)]c2
In the case of formation of a nucleus, the evolution of energy equal to the binding energy of the nucleus takes place due to the disappearance of a fraction of the total mass. If the quantity of mass disappearing is ΔM, then the binding energy is
BE = ΔMc2
From the above discussion, it is clear that the mass of the nucleus must be less than the sum of the masses of the constituent neutrons and protons. We can then write.
ΔM= [ZMp + (A-Z)Mn -M(A,Z)
Where M (A, Z) is the mass of the atom of mass number A and atomic number Z. Hence, the binding energy of the nucleus is
BE = [ZMp + (A-Z)Mn -M(A,Z)]c2
Where N = A -Z = number of neutrons.






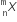 emits one α - particle and two β- particles. The resulting nucleus is
emits one α - particle and two β- particles. The resulting nucleus is 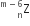
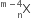
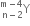
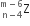
 mass represented by M (A, Z). If Mp and Mn denote the mass of proton and neutron respectively and BE the binding energy (in MeV), then:
mass represented by M (A, Z). If Mp and Mn denote the mass of proton and neutron respectively and BE the binding energy (in MeV), then: