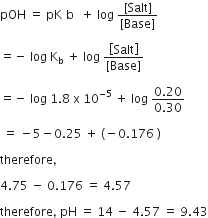A buffer solution is prepared in which the concentration of NH3 is 0.30 M and the concentration of NH4 is 0.20 M. If the equilibrium constant, Kb for NH3 equals 1.8 x 10-5, what is the pH of this solution?
log ( 2.7 = 0.43)
-
9.43
-
11.72
-
8.73
-
9.08
A.
9.43