Work, Energy And Power
Sponsor Area
A force  is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the
is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the 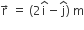 .The work done on the particle in joules is
.The work done on the particle in joules is
-
-7
-
+7
-
+10
-
+13
B.
+7
Work done in displacing the particle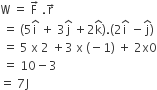
Sponsor Area
A particle of mass 100 g is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 5 m/s. the work done by the force of gravity during the time the particle goes up is
-
0.5 J
-
-0.5 J
-
−1.25 J
-
1.25 J
C.
−1.25 J
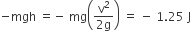
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up ? Fat supplies 3.8×107 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g=9.8 ms−2:
-
2.45 ×10−3 kg
-
6.45 x×10−3 kg
-
9.89 ×10−3 kg
-
12.89 ×10−3 kg
D.
12.89 ×10−3 kg
Given potential energy burnt by lifting weight
= mgh = 10 x 9.8 x 1 x 1000 = 9.8 x 104 J
If mass lost by a person be m, then energy dissipated
= m x 2 x 38 x 107 J /10
⇒ m = 5 x 10-3 x 9.8 / 3.8
= 12.89 x 10-3 kg
A spherical ball of mass 20 kg is stationary at the top of a hill of height 100 m. It rolls down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 30 m and finally rolls down to a horizontal base at a height of 20 m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is
-
40 m/s
-
20 m/s
-
10 m/s
-
10
 m/s
m/s
A.
40 m/s
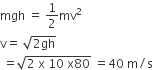
A uniform chain of length 2 m is kept on a table such that a length of 60 cm hangs freely from the edge of the table. The total mass of the chain is 4 kg. What is the work done in pulling the entire chain on the table?
-
7.2 J
-
3.6 J
-
120 J
-
1200 J
B.
3.6 J
Mass per length
= M/L
= 4/2 = 2 kg/m
The mass of 0.6 m of chain = 0.6 x 2 = 1.2 kg
The centre of mass of hanging part = 0.6 +0 /2 = 0.3 m
Hence, work done in pulling the chain on the table
W =mgh
= 1.2 x 10 x 0.3
= 3.6 J
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





