Kinetic Theory
Sponsor Area
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then
-
the momentum changes but the kinetic energy is constant
-
both momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are not constant
-
both, momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are constant
-
kinetic energy changes but the momentum is constant
A.
the momentum changes but the kinetic energy is constant
Sponsor Area
A gaseous mixture consists of 16 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen. The ratio cp/cv of the mixture is
-
1.59
-
1.62
-
1.4
-
1.54
B.
1.62
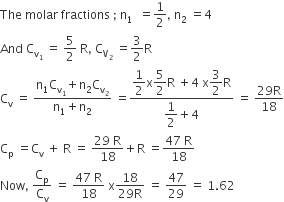
Cp and Cv are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. It is observed that
Cp – Cv = a for hydrogen gas
Cp – Cv = b for nitrogen gas
The correct relationship between a and b is
-
a = 14 b
-
a = 28 b
-
a = 1/14b
-
a= b
A.
a = 14 b
CP – CV = R
where CP and CV are molar specific heat capacities
As per the question
a= R/2
b= R/28
a= 14b
One mole of ideal monoatomic gas (γ = 5/30) is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas(γ = 7/5). What is γ for the mixture? γ denotes the ratio of specific heat at constant pressure, to that at constant volume.
-
3/2
-
23/15
-
35/23
-
4/3
A.
3/2
Q = Q1 + Q2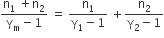
The speed of sound in oxygen (O2) at a certain temperature is 460 ms−1. The speed of sound in helium (He) at the same temperature will be (assumed both gases to be ideal)
-
1420 ms−1
-
550 ms−1
-
375 ms−1
-
650 ms−1
A.
1420 ms−1
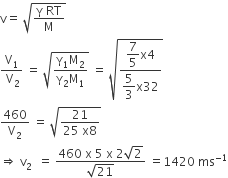
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





