The Solid State
Sponsor Area
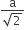
A metal crystallises in a face centred cubic structure. If the edge length of its unit cell is'a', the closest approach between two atoms in metallic crystal will be
-
2a
-

-

-
D.
In FCC unit cell atoms are in constant along face diagonal
So, √2a = 4R
therefore, the closest distance
![]()
Sponsor Area
An ionic compound has a unit cell consisting of A ions at the corners of a cube and B ions on the centres of the faces of the cube. The empirical formula for this compound would be
-
A2B
-
AB
-
AB3
-
A3B
C.
AB3
Based on lattice energy and other considerations which one of the following alkali metal chlorides is expected to have the highest melting point.
-
LiCl
-
NaCl
-
KCl
-
RbCl
B.
NaCl
Although lattice energy of LiCl higher than NaCl but LiCl is covalent in nature and NaCl ionic thereafter, the melting point decreases as we move NaCl because the lattice energy decreases as a size of alkali metal atom increases (lattice energy ∝ to melting point of alkali metal halide)
Copper crystallizes in fcc with a unit cell length of 361 pm. What is the radius of copper atom?
-
108 pm
-
127 pm
-
157 pm
-
181 pm
B.
127 pm
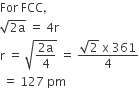
CsCl crystallises in body centred cubic lattice. If 'a' its edge length, then which of the following expression is correct?
C.
In CsCl, Cl- lie at corners of simple cube and Cs+ at the body centre, Hence, along the body diagonal, Cs+ and Cl- touch each other so

Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





