Surface Chemistry
Sponsor Area
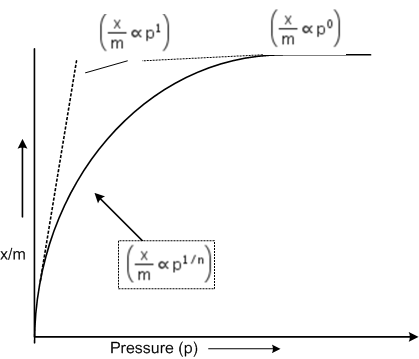
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following is correct?
-
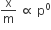
-
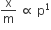
-
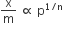
-
All of the above are correct for a different range of pressure
D.
All of the above are correct for a different range of pressure

Sponsor Area
For a linear plot of log (x/m) versus log p in a Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following statements is correct? (k and n are constants)
-
1/n appears as the intercept.
-
Only 1/n appears as the slope.
-
log (1/n) appears as the intercept.
-
Both k and 1/n appear in the slope term
B.
Only 1/n appears as the slope.
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm,
![]()
On taking logarithm both sides, we get
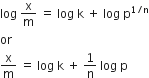

![]() c= intercept = log k, m =slope = 1/n and x = log p
c= intercept = log k, m =slope = 1/n and x = log p
Gold numbers of protective colloids A, B, C and D are 0.50, 0.01, 0.10 and 0.005, respectively. The correct order of their protective powers is
-
D < A < C < B
-
C < B < D < A
-
A < C < B < D
-
B < D < A < C
C.
A < C < B < D
Higher the gold number lesser will be the protective power of colloid.
The coagulating power of electrolytes having ions Na+, Al3+ and Ba2+ for arsenic sulphide sol increases in the order:
-
Al3+<Ba2+<Na+
-
Na+<Ba2+<Al3+
-
Ba2+< Na2+<Al3+
-
Al3+< Na+<Ba2+
B.
Na+<Ba2+<Al3+
As2S3 is an anionic sol (negative sol) hence coagulation will depend upon coagulating power of cation, which is directly proportional to the valency of cation (Hardy-Schulze rule).
The disperse phase in colloidal iron (III) hydroxide and colloidal gold is positively and negatively charged, respectively, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
-
magnesium chloride solution coagulates, the gold sol more readily than the iron (III) hydroxide sol.
-
sodium sulphate solution causes coagulation in both sols
-
mixing the sols has no effect
-
coagulation in both sols can be brought about by electrophoresis
C.
mixing the sols has no effect
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





