Structure Of Atom
Sponsor Area
A gas absorbs a photon of 355 nm and emits at two wavelengths. If one of the emission is at 680 nm, the other is at
-
1035 nm
-
325 nm
-
743 nm
-
518 nm
C.
743 nm
E = E1 + E2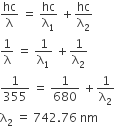
Sponsor Area
A stream of electrons from a heated filament was passed between two charged plates kept at a potential difference V esu. If e and m are charge and mass of an electron, respectively, then the value of h/λ (where λ is wavelength associated with electron wave) is given by:
-
2meV
-

-

-
mev
C.

The relation between h/λ and energy is given as:
Applying de-Broglie wavelength and kinetic energy term in eV.
de-Broglie wavelength for an electron (λ) = h/p
⇒ p = h/ λ (i)
Kinetic energy of an electron = eV
As we know that,
From equations (i) and (ii), we get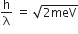
According to Bohr’s theory, the angular momentum of an electron in 5th orbit is
-
25h/ π
-
1.0h/π
-
10/π
-
2.5h/π
D.
2.5h/π
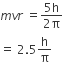
Calculate the wavelength (in nanometer) associated with a proton moving at 1.0 × 103 ms–1
(Mass of proton = 1.67 × 10–27 kg and h = 6.63 ×10–34Js)
-
0.032 nm
-
0.40 nm
-
2.5 nm
-
14.0 nm
B.
0.40 nm
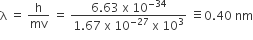
Consider the ground state of Cr atom (Z = 24). The number of electrons with the azimuthal quantum numbers I =1 and 2 are respectively
-
12 and 4
-
16 and 5
-
16 and 4
-
12 and 5
D.
12 and 5
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





