Hydrogen
Sponsor Area
From the following statements regarding H2O2, choose the incorrect statement:
-
It can act only as an oxidising agent
-
It decomposed on exposure to light
-
It has to be stored in plastic or wax lined glass bottles in dark
-
It has to be kept away from dust
A.
It can act only as an oxidising agent
Hydrogen peroxide acts as both reducing as well oxidising agent.
Sponsor Area
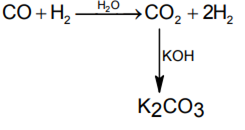
In context with the industrial preparation of hydrogen from water gas (CO + H2), which of the following is the correct statement?
-
CO and H2 are fractionally separated using differences in their densities
-
CO is removed by absorption in aqueous Cu2Cl2 solution
-
H2 is removed through occlusion with Pd
-
CO is oxidised to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of CO2 in alkali
D.
CO is oxidised to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of CO2 in alkali
In which of the following reactions H2O2 acts as a reducing agent?
I. H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- →2H2O
II. H2O2 - 2e- →O2 + 2H+
III. H2O2 +2e-→ 2OH-
IV. H2O2+ 2OH- -2e- →O2 + 2H2O
-
I and II
-
III and IV
-
I and III
-
II and IV
D.
II and IV
The release of the electron is known as reduction. So, H2O2 acts as a reducing agent when it releases electrons.
Here, in reactions (II) and (IV), H2O2 release two electrons, hence reactions (II) and (IV) is known as reduction. In reactions (I) and (III), two electrons are being added so (I) and (III) represents oxidation.
The concentration of fluoride, lead, nitrate and iron in a water sample from an underground lake was found to be 1000 ppb, 40 ppb, 100 ppm and 0.2 ppm, respectively. This water is unsuitable for drinking due to the high concentration of:
-
Lead
-
Nitrate
-
Iron
-
Fluoride
B.
Nitrate
This water unsuitable for drinking due to the high concentration of nitrate. In drinking water, maximum permissible concentration of
Lead = 50 ppm
Nitrate = 50 ppm
Iron = 0.2 ppm
Fluoride = 1 ppm
Very pure hydrogen (99.9%) can be made by which of the following processes?
-
Reaction of methane with steam
-
Mixing natural hydrocarbons of high molecular weight
-
Electrolysis of water
-
Reaction of salt like hydrides with water
C.
Electrolysis of water
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





