Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers
Sponsor Area
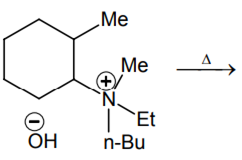
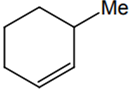
The alkene formed as a major product in the above elimination reaction is
-

-
CH2 = CH2
-
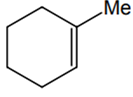
-
CH2 = CH2


B.
CH2 = CH2
Sponsor Area
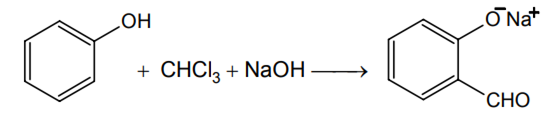
The electrophile involved in the above reaction is
-
dichloromethyl cation (C+HCl )
-
dichlorocarbene ( :CCl2)
-
trichloromethyl anion (C-Cl3 )
-
formyl cation (C+HO)
dichloromethyl cation (C+HCl )
dichlorocarbene ( :CCl2)
trichloromethyl anion (C-Cl3 )
formyl cation (C+HO)
B.
dichlorocarbene ( :CCl2)
A solution of (–) –1 – chloro –1 – phenylethane is toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5, due to the formation of
-
carbanion
-
Carbene
-
Carbocation
-
free radical
C.
Carbocation
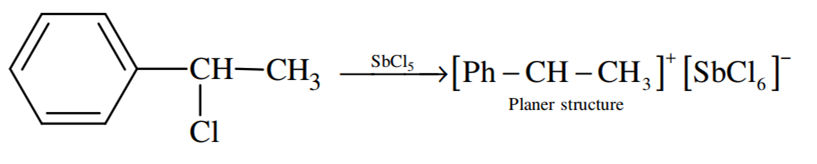
Because of the planar structure of carbonation, both retention and inversion can take place.
Acetyl bromide reacts with excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl given
-
acetone
-
acetyl iodide
-
2- methyl -2- propanol
-
acetamide
C.
2- methyl -2- propanol

Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes except ethene leads to the formation of
-
primary alcohol
-
secondary or tertiary alcohol
-
mixture of primary and secondary alcohols
-
mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
D.
mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





