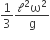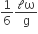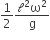Sponsor Area
System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Determine the volume of 1 mole of any gas at S.T.P., assuming it behaves like an ideal Gas.
1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 dm3 at stp (standard temperature and pressure, taken as 0°C and 1 atmosphere pressure). You may also have used a value of 24.0 dm3 at room temperature and pressure (taken as about 20°C and 1 atmosphere).
These figures are actually only true for an ideal gas, and we'll have a look at where they come from.
We can use the ideal gas equation to calculate the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at 0°C and 1 atmosphere pressure.
First, we have to get the units right.
0°C is 273 K. T = 273 K
1 atmosphere = 101325 Pa. p = 101325 Pa
We know that n = 1, because we are trying to calculate the volume of 1 mole of gas.
And, finally, R = 8.31441 J K-1 mol-1.
Slotting all of this into the ideal gas equation and then rearranging it gives:
And finally, because we are interested in the volume in cubic decimetres, you have to remember to multiply this by 1000 to convert from cubic metres into cubic decimetres.
The molar volume of an ideal gas is therefore 22.4 dm3 at stp.
And, of course, you could redo this calculation to find the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at room temperature and pressure - or any other temperature and pressure.
- how does carnot cycle operates
- why does absolute zero not correspond to zero energy
- The Carnot cycle consists of the following four processes: A reversible isothermal gas expansion process. In this process, the ideal gas in the system absorbs qin amount heat from a heat source at a high temperature Th, expands and does work on surroundings.
-
As you know , absolute zero means the temperature in Kelvin scale is 0K or in Celcius scale is -273.15°C . actually, in this temperature, Gaseous molecule be rest , there is no motion of molecule in their position. due to this reason we say that energy of Gaseous molecule at this is zero. means absolute zero correspond to zero energy .
well, it's hard to achieve Absolute zero or 0K or -273.15°C temperature. it is just theoretical. molecular can't achieve Absolute zero.
A thin uniform rod of length
D.
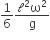
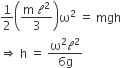
Let P(r) = Qr/πR4 be the charge density distribution for a solid sphere of radius R and total charge Q. for a point ‘p’ inside the sphere at distance r1 from the centre of the sphere, the magnitude of electric field is
-

-
0
-
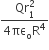
-
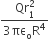
C.
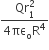
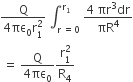
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series