Sponsor Area
The Government : Budget And The Economy
What is a government budget?
Meaning of a Government Budget. “A government budget is an annual statement of the estimated receipts and expenditure of the government during a fiscal year.' Just as your household budget is all about what you earn and spend, similarly the government budget is a statement of government income and expenditure. The government first plans expenditure according to its objectives and then tries to raise resources to meet the proposed expenditure. Thus, a budget is a statement of anticipated expenditure under various heads and proposed resources of financing the expenditure for the ensuring financial year. The financial (fiscal) year starts on April 1 and ends on March 31 of next year. For example, fiscal or budget year 2010-11 is from April 1, 2010 to March 31, 2011. In India, on last day of February, the Finance Minister presents annual budget of the government in the Lok Sabha for its approval. Again it needs to be noted that government cannot make expenditure under this budget unless budget is approved by the Parliament. Needless to mention that budget is the most important document as according to Keynes budgetary policies play a significant role in stabilisation of the economy.
State objectives of government budget?
or
How can a government budget help in reducing inequalities through redistribution of income? Explain.
or
Explain 'allocation of resources' objective of governent budget.
Objectives of a Government Budget. Briefly put, promoting rapid and balanced economic development with equality and social justice has been the general objective of all our policies and plans. General objectives of a government budget are as under:
(i) Economic growth. To promote rapid and balanced economic growth so as to improve living standard of the people. Economic growth implies increasing capacity of the economy to produce more goods and services. Public welfare is the main guide.
(ii) Reduction of Poverty and Unemployment. To eradicate mass poverty and unemployment by creating maximum employment opportunities and providing maximum social benefits to the poor. Social welfare is the single most objective of the government. Every Indian should be able to meet his basic needs like food, clothing, housing along with decent health care and educational facilities.
(iii) Reallocation of Resources. (A 2010, D 2011) To reallocate resources in line with social and economic objectives, government has to allocate resources into areas where private sector is not coming, e.g., sanitation, water supply, rural development, education, health, etc. Moreover, government provides more funds to productive sectors and draws away resources from some other sectors to promote balanced economic growth of different regions.
(iv) Reduction of inequalities/Redistribution of income. To reduce inequalities of income and wealth government can influence distribution of income through levying taxes on the rich and granting subsidies to poor. Government uses progressive taxation policy, i.e., high rate of tax on rich people and lower rate on lower income group. Government provides subsidies and amentities to people whose income level is low. More, emphasis is laid on equitable distribution of wealth and income. Economic progress in itself is not a sufficient goal but goal must be equitable progress.
(v) Price Stability/Economic stability. Government can bring economic stability i.e. can control fluctuations in general price level through taxes, subsidies and expenditure. For instance when there is inflation (continuous rise in prices), govt. can reduce its expenditure and when there is depression characterised by following output and prices, govt. can reduce taxes and grant subsidies to encourage spending by people.
(vi) Management of public enterprises. To manage, public enterprises which are of the nature of monopolies like railways, electricity, etc.
Impact of the budget. A budget impacts the society at three levels: (i) It promotes aggregate fiscal discipline through controlled expenditure, given the quantum of revenues. (ii) Resources of the country are allocated on the basis of social priorities. (iii) It contains effective and efficient programmes for delivery of goods and services to achieve its targets and goals. In short, the budget impacts the economy through aggregate fiscal discipline, resource allocation and provision of programmes for delivery of services.
Explain the two components (revenue budget and capital budget) of government budget.
Components of the budget. The budget is divided into two parts — (i) Revenue Budget, and (ii) Capital Budget.
(i) The Revenue Budget comprises current revenue receipts and current expenditure met from such revenues. The revenue receipts include both tax revenue (like income tax, excise duty) and non-tax revenue (like interest receipts, profits). (ii) Capital Budget consists of capital receipts (like borrowing, disinvestment) and capital expenditure (creation of assests, investment) of the government. Capital receipts are receipts of the government which create liabilities or reduce assets. Capital expenditure is the expenditure of the government which either reduces liability or creates an asset. Thus, capital budget is an account of assets and liabilities of the government which takes into consideration changes in capital.
The structure (or components) of a government budget broadly consists of two parts — Budget Receipts and Budget Expenditure as shown in the following chart. Let us see their classification.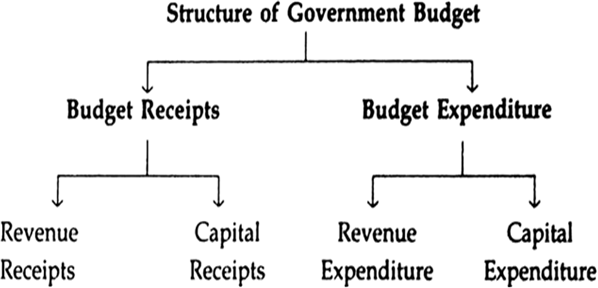
What do you understand by Budget Receipts (Govt. Receipts)? Describe its two types.
Meaning. Budget receipts refer to estimated money receipts of the government from all the sources during a fiscal year. It shows the sources from where the government intends to get money to finance the expenditure (both revenue and capital expenditure). Budget receipts are of two types — Revenue Receipts and Capital Receipts — as explained below. Their components are shown in the following chart.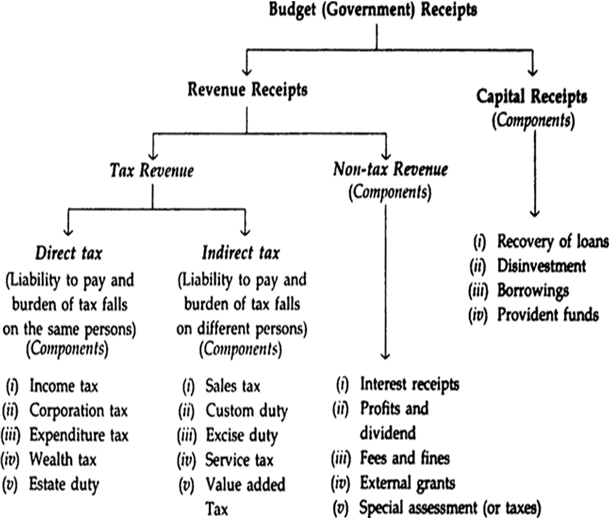
Note: According to Government Budget for 2010-11, Receipt of 1 Rupee conies from: Income tax 9 paise, corporation tax 23 paise, custom duty 9 paise, excise duty 10 paise, services and other taxes 6 paise, Non-taxes Revenue 11 paise, borrowing and other liability 29 paise, non-debt Capital receipts 3 paisa = 100 paise.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





