Sponsor Area
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
a) When an unpolarized light falls on a polaroid, only those electric vectors that are oscillating along a direction perpendicular to the aligned molecules will pass through. Thus, incident light gets linearly polarized.
Electric vectors which are along the direction of the aligned molecules gets absorbed.
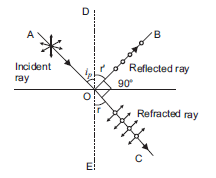
Whenever unpolarized light is incident on the boundary between two transparent media, the reflected light gets partially or completely polarized. When reflected light is perpendicular to the refracted light, the reflected light is a completely polarized light.
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index 3/2, placed in water of refractive index 4/3. Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
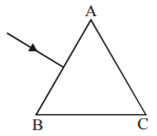
No, it will not suffer total internal reflection
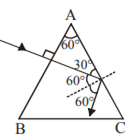
so if i is less than 60o then TIR will not happen
A symmetric biconvex lens of the radius of curvature R and made of glass of refractive index 1.5, is placed on a layer of liquid placed on top of a plane mirror as shown in the figure. An optical needle with its tip on the principal axis of the lens is moved along the axis until its real, inverted image coincides with the needle itself. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured to be x. On removing the liquid layer and repeating the experiment, the distance is found to bey. Obtain the expression for the refractive index of the liquid in terms of x and y.
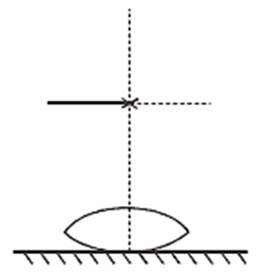
Let,
f = focal length liquid +lens
f1 = focal length of lens
f2 = focal length of liquid mirror
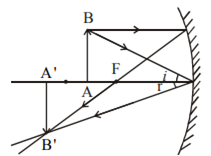
Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object.
Ray Diagram:
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





