Sponsor Area
Application of Integrals
A retired person wants to invest an amount of Rs. 50, 000. His broker recommends investing in two type of bonds ‘A’ and ‘B’ yielding 10% and 9% return respectively on the invested amount. He decides to invest at least Rs. 20,000 in bond ‘A’ and at least Rs. 10,000 in bond ‘B’. He also wants to invest at least as much in bond ‘A’ as in bond ‘B’. Solve this linear programming problem graphically to maximise his returns.
Maximize Z = 0.1x + 0.09 y
x + y ≤ 50000
x ≥ 20000
y ≥ 10000
y ≤ x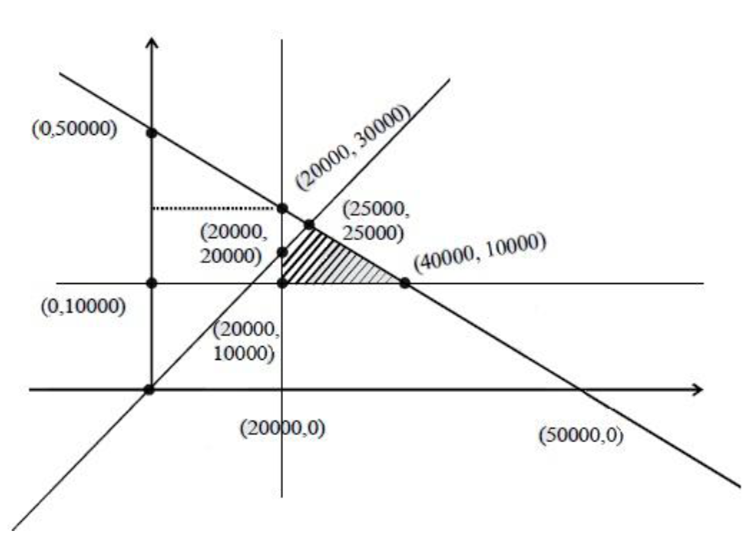
|
|
z=0.1 x+0.09y |
|
P1 (20000,10000) |
2900 |
|
P2(40000,10000) |
4900 |
|
P3(25000,25000) |
4750 |
|
P4(20000,20000) |
3800 |
when A invest 400000 & B invest 10000 his return is maximum.
Minimum and maximum z = 5x + 2y subject to the following constraints:
x – 2y ≤ 2
3x + 2y ≤ 12
−3x + 2y ≤ 3
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
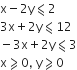
Converting the inequations into equations, we obtain the lines
x – 2y = 2…..(i)
3x + 2y = 12……(ii)
−3x + 2y = 3……(iii)
x = 0, y = 0
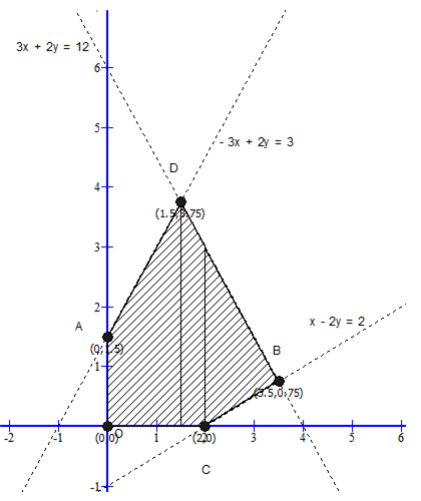
From the graph, we get the corner points as
A(0, 5), B(3.5, 0.75), C(2, 0), D(1.5, 3.75), O(0, 0)
The values of the objective function are:
| Point (x,y) | Values of the objective function Z= 5x+2y |
| A(0, 5) | 5 × 0 + 2 × 5 = 10 |
| B(3.5, 0.75) | 5 x 3.5 +2 x 0.75 =19 (Maximum) |
| C(2, 0) | 5 x 1.5 +2 x 3.75 =15 |
| O(0,0) | 5 x 0 + 2 x 0 = 0 (Minimum) |
Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the triangle whose vertices are (-1, 2), (1, 5) and (3, 4).
Consider the vertices, A(-1, 2), B(1, 5) and C(3, 4).
Let us find the equation of the sides of the triangle 
Thus, the equation of AB is: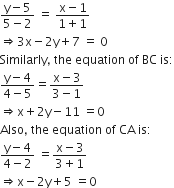
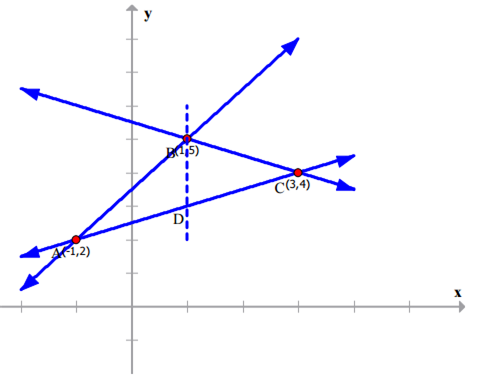
Now the area of  = Area of
= Area of  + Area of
+ Area of 

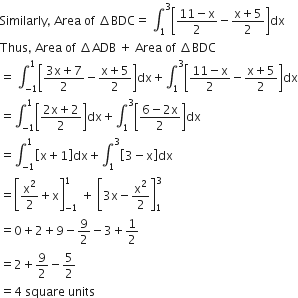
Using integration, find the area bounded by the curve x2 = 4y and the line x = 4y – 2.
The shaded area OBAO represents the area bounded by the curve x2 = 4y and the line x = 4y – 2.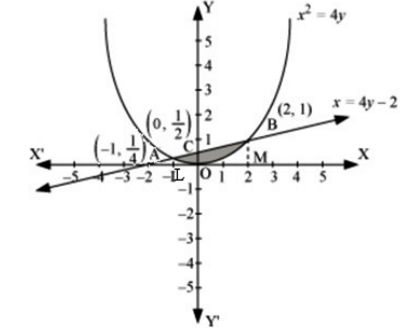
Let A and B be the points of intersection of the line and parabola.
Co-ordinates of point A are 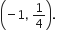 Co-ordinates of point B are (2, 1).
Co-ordinates of point B are (2, 1).
Area OBAO = Area OBCO + Area OACO ...(1)
Area OBCO = 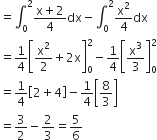
Area OACO =
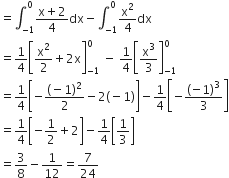
Therefore, required area = 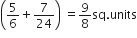
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





