Sponsor Area
Relative Molecular Mass And Mole
Define cryoscopic constant.
Cryoscopic constant is defined as the Molal depression constant Or it may be defined as the depression in freezing point when one mole of non-volatile solute is dissolved in one kilogram of solvent. Its units K Kg mol-1
Match the following:
| A. Colligative property | (i) Polysaccharide |
| B. Nicol prism | (ii) Aldol condensation |
| C. Activation energy | (iii) Ammonia |
| D. Starch | (iv) Polarimeter |
| E. Acetaldehyde | (v) Arrhenius equation |
A. Colligative property | (i) Ammonia |
B. Nicol prism | (ii) Polarimeter |
C. Activation energy | (iii) Arrhenius equation |
D. Starch | (iv) Polysaccharide |
E. Acetaldehyde | (v) Aldol condensation |
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze agent. Calculate the amount of ethylene glycol to be added to 4 kg of water of prevent it from freezing at -6°C. (Kf for H20 = 1.85 K mole-1 kg)
W =?
W = 4Kg =4000 gm
Kf =1.85
Freezing point of pure water =00 C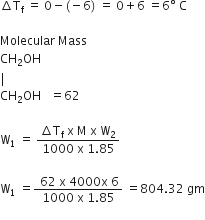
The freezing point of a solution containing 0.3 gms of acetic acid in 30 gms of benzene is lowered by 0.45K. Calculate the Van’t Hoff factor. (at. wt. of C = 12, H = 1, 0 =16, Kf for benzene = 5.12K kg mole-1)
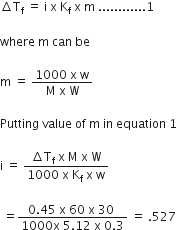
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





