Sponsor Area
Ionic Equilibria
(i)Give Lewis’ definition for acids and bases.
(ii) The solubility of Ag2CrO4 at 25°C is 8.0 x 10-5 moles /litre. Calculate its solubility product.
i) Lewis acid: A compound or an ionic species which can accept a pair of electron known as lewis acid.
Lewis base: A compound or an ionic species which can donate a pair of electron known as lewis base.
ii) Ag2CrO4 ⇌ 2Ag+ + CrO42‒
S 2s s
Ksp = [Ag+ ]2 [CrO42‒] = (2s)2 (s)
= 4s3 = 4 x (8 x 10‒5 )3 = 2.048 x 10‒12
The [OH-] concentration of a weak base is given by:
-
Ckb
-

-

-

Ckb



C.

If the ionization (dissociation) constant of acetic acid is ka, what will be the pH of a solution containing equal concentrations of acetic acid and sodium acetate?
For the equal concentration of acetic acid and sodium acetate in a solution. its pH will give by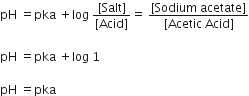
Match the following:
| A. Nernst equation | (i) Water |
| B. Water | (ii) Constant volume |
| C. Amphiprotic solvent | (iii) Ammonia |
| D. Lewis base | (iv) Optical Isomers |
| E. Isochoric process | (v) Electrochemical cells. |
A. Nernst equation | (i) Electrochemical cells. |
B. Water | (ii) Optical Isomers |
C. Amphiprotic solvent | (iii) Water |
D. Lewis base | (iv) Ammonia |
E. Isochoric process | (v) Constant volume |
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





