Sponsor Area
Photosynthesis
Each of the following questions / statements have four suggested answer. Rewrite the correct answer in each case:
Oxygen is released in photosynthesis by
-
Photophosphorylation
-
Photolysis of water
-
Photorespiration
-
Photons
B.
Photolysis of water
Explain the C4 cycle of photosynthesis.
Reactions taking place in mesophyll cell chloroplast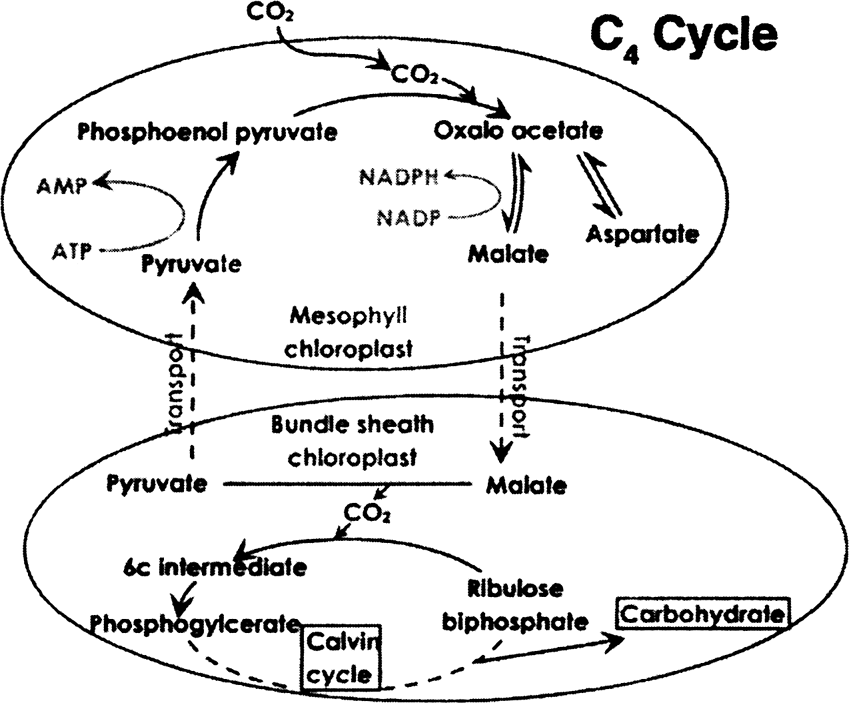
Reactions taking place in bundle sheath cell chloroplast.
Give scientific terms for each of the following :
Process of splitting of water molecules during photosynthesis.
Photolysis
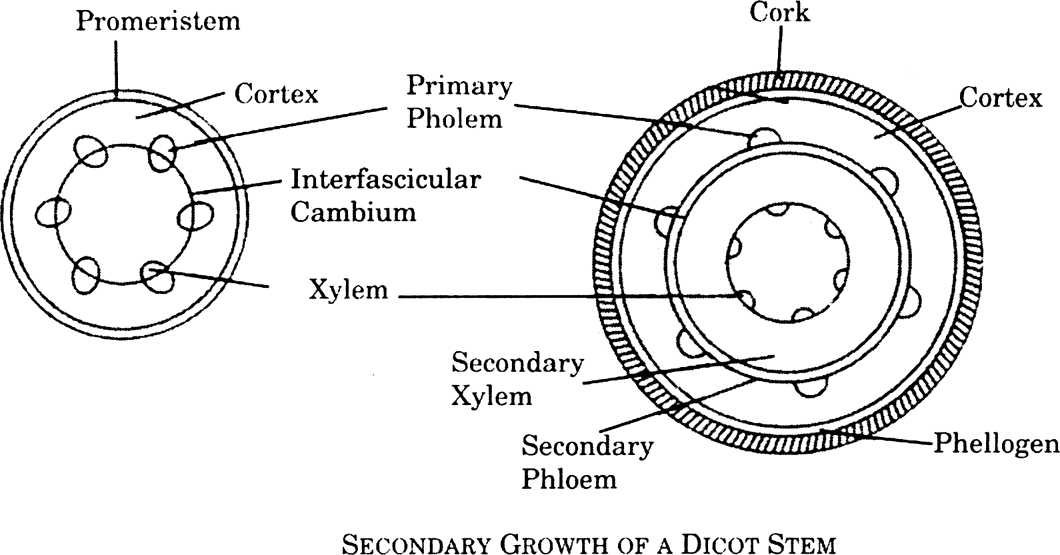
(a) Give an account of activity of cambium in the secondary growth of the stem.
(b) Write three differences between C3 and C4 cycles.
(c) Mention two advantages each of the following:
(i) Hydroponics (ii) Turgidity to plants (iii) Cross pollination
(a) Activity of cambium in the secondary growth of the stem:
(i) Formation of cambium rings: The vascular bundles of dicot stem have stripes of cambium in between xylem and phloem and is known as intrafascicular cambium.
During secondary growth, the cells of medullary rays in a line with the intrafascicular cambium develop merismatic activity and from stripes of cambium called interfascicular cambium. Both these form cambium ring or phellogen.
(ii) Formation of secondary tissues : This cambium ring becomes active a whole and starts cutting new cells. The cells differentiate to secondary xylem and phloem.
(iii) Secondary Medullary rays : Certain cells of cambium form some narrow bands of living parenchyma cells passing through secondary xylem and phloem are called secondary medullary rays.
(iv) Annual rings : The growth in successive years appears in the form of concentric rings or annual rings.
(b)
| C3 Plants | C4 Plants |
| RuBP is the CO2 acceptor. | PEP is the CO2 acceptor |
| First stable product is phosphoglyceric acid. | First stable product is oxaloacetic acid. |
| Kranz anatomy is not present | Kranz anatomy is present |
| Process is slow and less efficient | Process is fast and efficient |
(c)
(i) Advantages of hydroponics :
a. The importance of a particular element can be studied using the process
b. Through hydroponic gardening; plants can be grown anywhere as long as their growth requirements are met.
(ii) Turgidity to plants :
i. Turgidity helps to maintain the shape of the leaves.
ii. Turgid condition prevents wilting and allows more exposure to the sunlight.
(iii) Advantages of Cross pollination :
Cross pollination helps in creating the variation in species of plant.
Cross pollination results in the formation of new combinations.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





