In a Duma's nitrogen estimation method, 0.3 g of an organic compound gave 50 mL of nitrogen collected at 300K and 715 mm pressure. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the compound. (Aqueous tension of water at 300 K is 15 mm).
Mass of organic compound = 0.3 g
(i) To calculate the volume of nitrogen at N.T.P.
(Given) (At N.T.P.)
Applying the general gas equation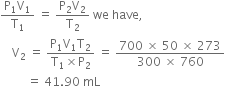
(ii) To calculate the percentage of nitrogen:
Now 22400 mL of nitrogen at N.T.P. weighs = 28 g.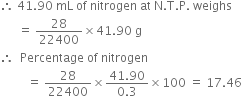






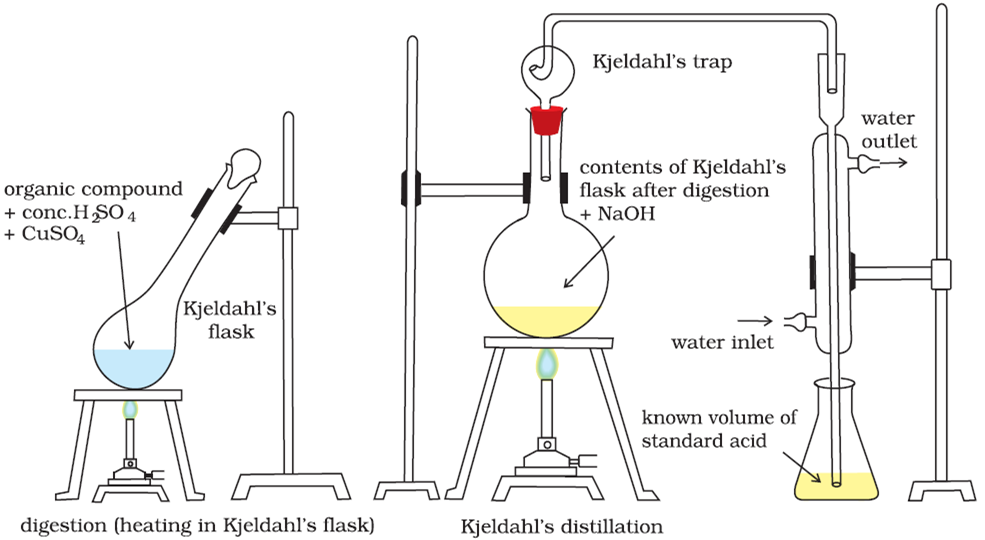
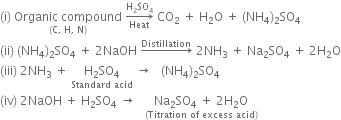
 taken
taken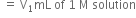
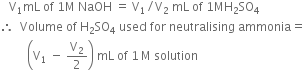

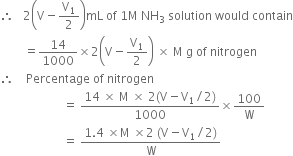
 required for neutralising ammonia = 10 mL
required for neutralising ammonia = 10 mL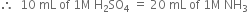
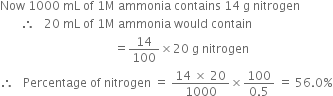
 60 mL of 0.5 M NaOH = 30 mL of 0.5 M
60 mL of 0.5 M NaOH = 30 mL of 0.5 M
