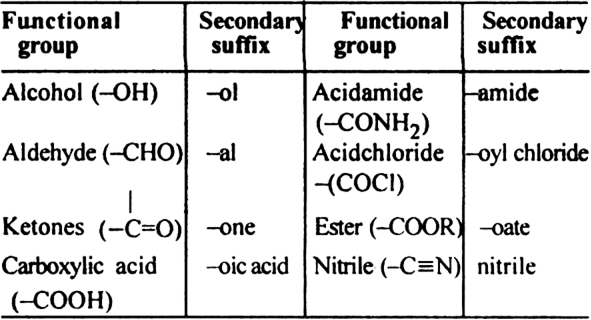
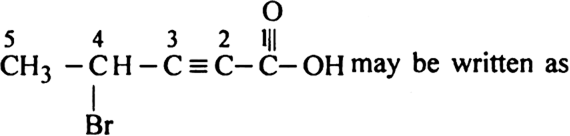What do you mean by nomenclature of aliphatic hydrocarbons?
The commonly adopted systems for naming organic compounds are:
(i) Common or Trivial system: In this system, the name of the organic compound is based on its origin/ history or some property. Though common names are short and easy to remember, yet a particular compound may be given a number of names. e.g. methyl alcohol is named wood-spirit because it is obtained by destructive distillation of wood.
2. IUPAC system: This is the best system for naming the aliphatic organic compounds. To evolve a systematic method of nomenclature, the international group of chemists have several conferences and recommended the most definite set of organic nomenclature rules called International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry rules (IUPAC rules). In the IUPAC system, name of organic compound consists of three parts:
(i) Word root (ii) Prefix (iii) Suffix.