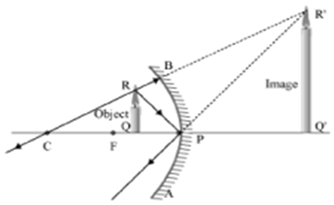
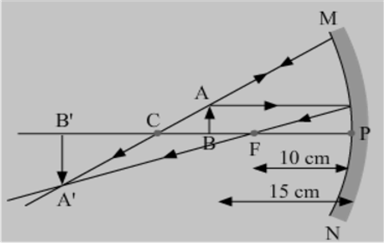
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
Two light rays whose path of reflection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light ray after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because the light ray is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.
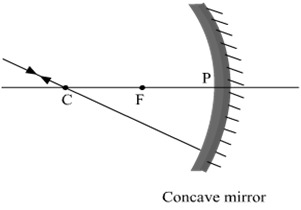
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.
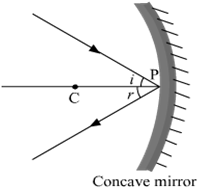
Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below: