If the distance between the points (4, k) and (1, 0) is 5, then what can be the possible values of k?
Let the points X (4,k) and Y(1,0)
It is given that the distance XY is 5 units.
By using the distance formula,
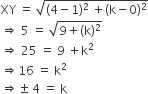
Sponsor Area
If the distance between the points (4, k) and (1, 0) is 5, then what can be the possible values of k?
Let the points X (4,k) and Y(1,0)
It is given that the distance XY is 5 units.
By using the distance formula,
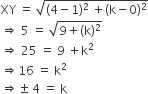
The area of a triangle is 5 sq units. Two of its vertices are (2, 1) and (3, –2). If the third vertex is (7/2, y), find the value of y.
Let A(x1, y1)=A(2, 1), B(x2, y2)=B(3,−2) and C(x3, y3)=C(7/2,y).
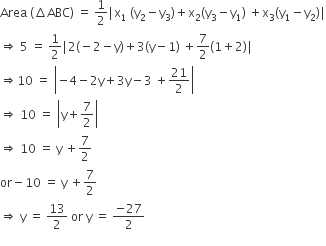
If a≠b≠0, prove that the points (a, a2), (b, b2) (0, 0) will not be collinear.
Let A(a, a2), B(b, b2) and C(0, 0) be the coordinates of the given points.
We know that the area of a triangle having vertices (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3, y3) is ∣∣12[x1(y2−y3)+x2(y3−y1)+x3(y1−y2)]∣∣ square units.
So,
Area of ∆ABC\
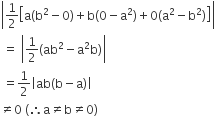
Since the area of the triangle formed by the points (a, a2), (b, b2) and (0, 0) is not zero, so the given points are not collinear.
let t line x-y-2=0 divid t line segment in t ratio k : 1 at point C
so coordinates of C are
![]()
C lies on x - y - 2 = o
so, subs coordinates of x,y in tis eq.
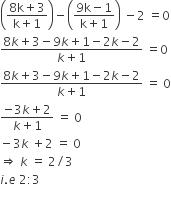
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series