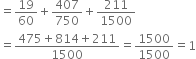In a cricket match, a batswoman hits a boundary 6 times out of 30 balls she plays. Find the probability that she did not hit a boundary.
Let E be the event of hitting the boundary.
Then,![]()
∴ Probability of not hitting the boundary
= 1 – Probability of hitting the boundary
= 1 – P(E) = 1 – 0.2 = 0.8.