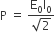The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
- Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for
power dissipation in this device. - Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
- Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
- Step up or step down transformer, Eddy current losses.
- With higher voltage, power losses are less, so voltage can be increased by the step-up transformer and the transformer works on A/c only.
- Both are interested towards technical knowledge and both are having sufficient ideas about power transmission.






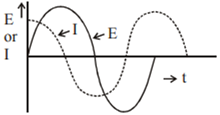
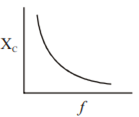
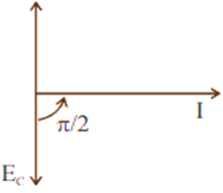
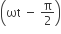 .The power consumption in the circuit is given by
.The power consumption in the circuit is given by