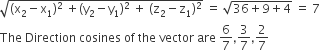The projections of a vector on the three coordinate axis are 6, - 3, 2 respectively. The direction cosines of the vector are
-
6, –3, 2
-
6/5, -3/5, 2/5
-
6/7, -3/7, 2/7
-
-6/7, -3/7, 2/7
C.
6/7, -3/7, 2/7
Projection of a vector on coordinate axis are
x2-x1, y2-y1, z2-z1
x2-x1 = 6, y2-y1 = -3, z2-z1 = 2