The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes g/9 (where g = the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth) in terms of R, the radius of the earth, is
-
2R
-

-
R/2
-

A.
2R
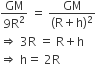
Sponsor Area
The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes g/9 (where g = the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth) in terms of R, the radius of the earth, is
2R

R/2

A.
2R
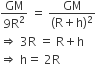
Sponsor Area
A planet in a distant solar system is 10 times more massive than the earth and its radius is 10 times smaller. Given that the escape velocity from the earth is 11 kms−1, the escape velocity from the
1.1 kms−1
11 kms−1
110 kms−1
0.11 kms−1
C.
110 kms−1
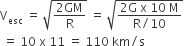
This question contains Statement -1 and Statement-2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement – I:
For a mass M kept at the centre of a cube of side ‘a’, the flux of gravitational field passing through its sides is 4π GM.
and
Statement – II
If the direction of a field due to a point source is radial and its dependence on the distance ‘r’ for the source is given as 1/r2, its flux through a closed surface depends only on the strength of the source enclosed by the surface and not on the size or shape of the surface
Statement – 1is false, Statement – 2 is true.
Statement – 1is true, Statement – 2 is true; Statement -2 is correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement – 1 is true, Statement – 2 is true; Statement -2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement – 1 is true, Statement – 2 is False.
B.
Statement – 1is true, Statement – 2 is true; Statement -2 is correct explanation for Statement-1.
g = GM/r2
If gE and gm are the accelerations due to gravity on the surfaces of the earth and the moon respectively and if Millikan’s oil drop experiment could be performed on the two surfaces, one will find the ratio (electronic charge on the moon/ electronic charge on the earth) to be
1
0
gE/gM
gM/gE
A.
1
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series