Sponsor Area
Human Eye and Colourful World
Discuss the reactivity of carbon in relation to its electronic configuration.
The electronic configuration of carbon is K (2), L (4). Thus it has 4 electrons in its outermost shell. In order to react or to achieve noble gas configuration, it should either gain or lose 4 electrons.
(i) It could gain four electrons forming C4– anion. But it would be diffcult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons, that is four extra electron.
(ii) It could lose four electron forming C4+ cation. But it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with six protons in its nucleus holding on to just two electrons.
Carbon overcomes above problem and forms a large number of compounds by sharing its valence electrons with other atoms of carbon or with atoms of other elements, thereby satisfying requirement to attain noble configuration of all the combining atoms. For example, carbon forms methane as shown below: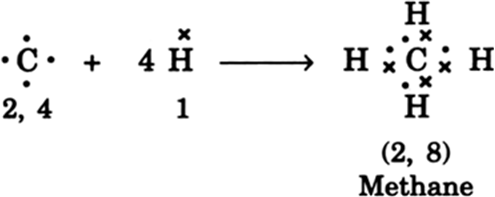
In methane, carbon shares its four valence electrons with four valence electrons, one each from four hydrogen atoms. Thus carbon attains the configuration 2, 8 as that of nearest noble gas, neon. And all four hydrogen atoms individually atttain the configuration of helium gas. Bond so formed due to sharing of electrons is called covalent bond.
What is a covalent bond?
The covalent bond is said to be formed when two atoms achieve stability by sharing of an electron pair, each contributing one electron to the electron-pair. In this way, the atoms can be regarded as having acquired a noble gas configuration.
For example: H2, hydrogen is formed due to sharing of electron between two atom of hydrogen.![]()
Taking a simple example, explain how the formation of covalent bond between two atoms brings stability to the molecule formation.
Take the example of formation of hydrogen molecule. When two hydrogen atoms come close together, nucleus of one atom exerts an attractive force on the electrons of the other atom and vice versa to complete their octet. This brings the two atoms still closer and potential energy decreases. At a particular distance between the two atoms, potential energy becomes minimum. Hydrogen atoms cannot come further closer because then the repulsive forces come into operation and cause the energy to increase. This stage of minimum energy which binds the two hydrogen atoms to form a molecule is actually the covalent bond.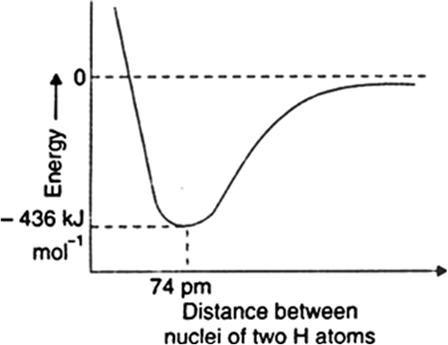
Explain the formation of covalent bonds in (i) chlorine molecule; (ii) carbon tetrachloride and (iii) ammonia.
(i) Formation of chlorine molecule: Two chlorine atoms share one electron of each and acquire stable electronic configuration as shown: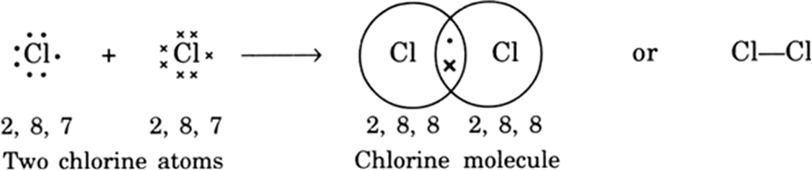
(ii) Formation of carbon tetrachloride: Carbon atoms has four electrons in the outermost shell. In the formation of carbon tetrachloride, it shares four electrons with four chlorine atoms. In turn four chlorine atoms share one electron each with one carbon atom. Thus in all, one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms complete their octet by mutual sharing of electrons and carbon tetrachloride containing four covalent bonds is formed as shown:
(iii) Formation of ammonia molecule: Nitrogen (N) atom has 5 electrons (2, 5) in the outermost shell. It shares one electron each of three hydrogen atoms to form ammonia molecule as shown:
One unshared pair of electrons in ammonia molecule is not involved in bond formation and is called a lone pair of electrons.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





