Sponsor Area
Triangles
In quadrilateral ACBD, AC = AD and AB bisects ∠A (See the given figure). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔABD. What can you say about BC and BD?
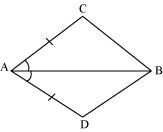
In ΔABC and ΔABD,
AC = AD (Given)
∠CAB = ∠DAB (AB bisects ∠A)
AB = AB (Common)
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔABD (By SAS congruence rule)
∴ BC = BD (By CPCT)
Therefore, BC and BD are of equal lengths.
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (See the given figure). Prove that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
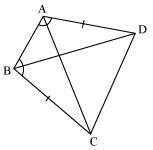
In ΔABD and ΔBAC,
AD = BC (Given)
∠DAB = ∠CBA (Given)
AB = BA (Common)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC (By SAS congruence rule)
∴ BD = AC (By CPCT)
And, ∠ABD = ∠BAC (By CPCT)
AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB (See the given figure). Show that CD bisects AB.
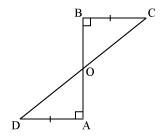
In ΔBOC and ΔAOD,
∠BOC = ∠AOD (Vertically opposite angles)
∠CBO = ∠DAO (Each 90º)
BC = AD (Given)
∴ ΔBOC ≅ ΔAOD (AAS congruence rule)
∴ BO = AO (By CPCT)
⇒ CD bisects AB.
l and m are two parallel lines intersected by another pair of parallel lines p and q (see the given figure). Show that ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA.
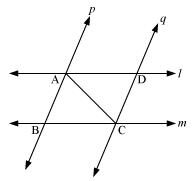
In ΔABC and ΔCDA,
∠BAC = ∠DCA (Alternate interior angles, as p || q)
AC = CA (Common)
∠BCA = ∠DAC (Alternate interior angles, as l || m)
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔCDA (By ASA congruence rule)
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





