Sponsor Area
Introduction to Mathematical Modelling
In a cricket match, a batswoman hits a boundary 6 times out of 30 balls she plays. Find the probability that she did not hit a boundary.
Let E be the event of hitting the boundary.
Then,![]()
∴ Probability of not hitting the boundary
= 1 – Probability of hitting the boundary
= 1 – P(E) = 1 – 0.2 = 0.8.
1500 families with 2 children were selected randomly, and the following data were recorded:
|
Number of girls in a family |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Number of families |
475 |
814 |
211 |
Compute the probability of a family, chosen at random, having
(0 2 girls (ii) 1 girl (iii) No girl.
Also check whether the sum of these probabilities is 1.
Total number of families
= 475 + 814 + 211 = 1500
(i) Probability of a family, chosen at random,
having 2 girls = ![]()
(ii) Probability of a family, chosen at random,
having 1 girl ![]()
(iii) Probability of a family, chosen at random,
having no girl ![]()
Sum of these probabilities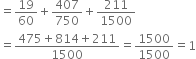
Hence, the sum is checked.
In a particular section of Class IX, 40 students were asked about the months of their birth, the following graph was prepared for the data so obtained. Find the probability that a student of the class was bom in August.
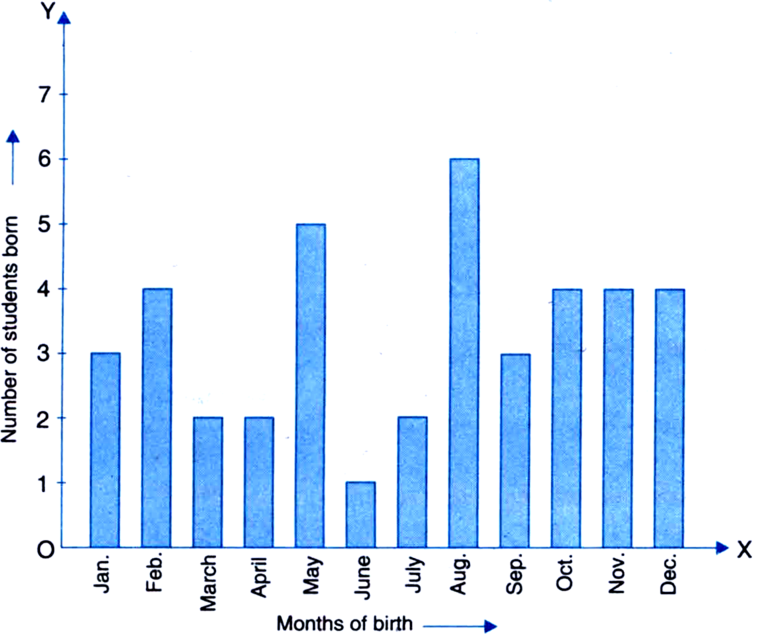
Total number of students bom in the year =3+4+2+2+5+1+2+6+3+4+4+4=40
Number of students bom in August = 6
∴ Probability that a student of the class was
born in August = ![]()
Three coins are tossed simultaneously 200 times with the following frequencies of different outcomes:
|
Outcome |
3 heads |
2 heads |
1 head |
No head |
|
Frequency |
23 |
72 |
71 |
28 |
If the three coins are simultaneously tossed again, compute the probability of 2 heads coming up.
Total number of times the three coins are tossed = 200
Number of times when 2 heads appear = 72
∴ Probability of 2 heads coming up![]()
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





