Sponsor Area
Mechanical Properties of Solids
State hooke’s law?
Hooke’s law states that the extension produced in the wire is directly proportional to the load applied within the elastic limit i.e. Acc to Hooke’s low Stress α Strain Stress = E x Strain E = Modulus of elasticity
Define modulas of elasticity and write down its Unit and Dimensions.
Modulus of elasticity = Stress / Strain, As Strain is a dimensionless quantity being a ratio between change in dimension to the original dimension, the dimensions of Modulus of Elasticity are the same as that of stress. That is kg/mm^2 are the dimensions of Modulus of Elasticity.
Write down the relation beween three types of moduli and poissons ration?
3 Types of Elastic Moduli. Young's modulus (E) describes tensile elasticity, or the tendency of an object to deform along an axis when opposing forces are applied along that axis; it is defined as the ratio of tensile stress to tensile strain. It is often referred to simply as the elastic modulus.
One kg of a diatomic gas is at a pressure of 8 × 104 N/m2 . The density of the gas is 4 kg/m-3. What is the energy of the gas due to its thermal motion?
-
3 × 104 J
-
5× 104 J
-
6× 104 J
-
7× 104 J
B.
5× 104 J
Thermal energy corresponds to internal energy
Mass = 1 kg
density = 8 kg/m3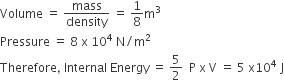
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





