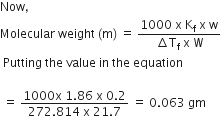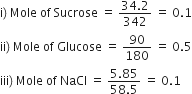Osmotic Pressure. The pressure which is applied to the solution in order to prevent the passage of solvent into it through a semi-permeable membrane present between the two is termed as osmotic pressure.
We know that osmotic pressure is a colligative property and hence it depends on the number of solute particles.
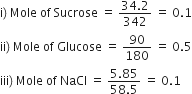
Since 1 mole = 6.023 x 1023 particles
So Sucrose = 6.023 x 1022 particles
(As Sucrose and Glucose are undissociated)
Glucose = 30.115 x 1022 particles
NaCl = 12.046 x 1022 particles.
(NaCl dissociates to give two ions)
Hence, the increasing order of their osmotic pressure is, Sucrose < NaCl < Glucose.