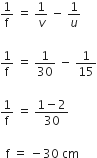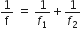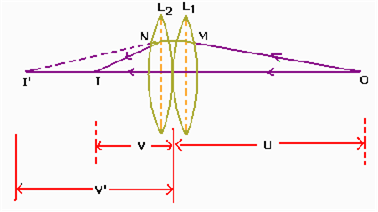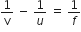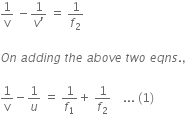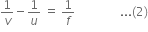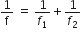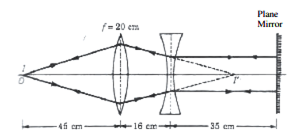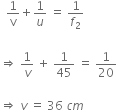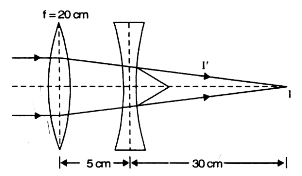
Calculate the focal length of a concave lens with the help of the above ray diagram. Focal length of convex lens is 20 cm.
Object distance, u = +15 cm
Image distance, v = 30 cm
Therefore, focal length is given by,