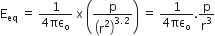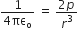Obtain an expresssion for intensity of electric field in end on position. i.e., axial position of an electric dipole.
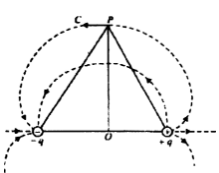
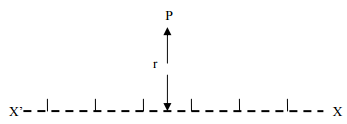
Let an electric dipole is taken which constitutes (+q) and (- q) charge separated by the distance 2l.
Let from the mid point of the dipole at a distance ‘r’ is the point P at intensities due to (+q) and (-q) charge respectively. direction along the dipole axis.
direction along the dipole axis.
E2 = 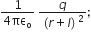 direction opposite to the dipole axis.
direction opposite to the dipole axis.
Resultant electric field intensity E = E1 - E2
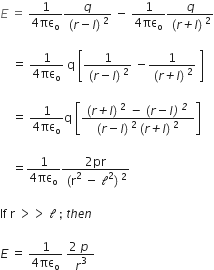






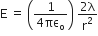
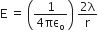
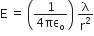
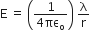
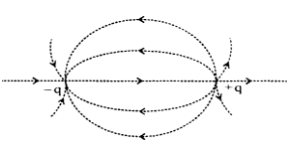

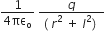
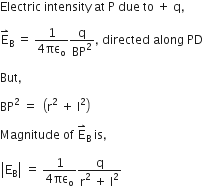
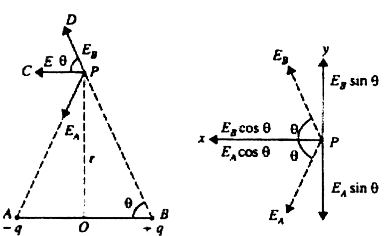
 .
.