Explain the following with suitable examples:
Ferromagnetism.
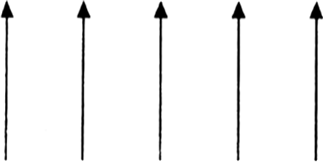
Fig. Schematic alignments of magnetic moments in ferromagnetism.

Ferrimagnetism:
This effect is observed when the magnetic moments of the domains in the substance are aligned in parallel and anti–parallel directions in unequal numbers. Ferrimagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnetic field as compared to ferromagnetic substances. Magnetite like Fe3O4 and ferrites like MgFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 are examples 
Piezoelectric effect (or pressure electricity):
The word piezoelectricitymeans electricity resulting from pressure.
Insulators do not conduct electricity be the electrons present in them are held tightly to the individual atoms or ions and do not move. However, when an electric field is applied polarisation takes place and newly formed dipoles may align themselves in an ordered manner so that such crystals have a net moment.
When mechanical stress is applied on a polar crystals so as to deform them, electricity produced due to displacement of ions. This is known as piezoelectric effect and electric so this produced is known as Piezo electricity or pressure electricity. Example are : titanium, barium and lead, lead zirconate (PbZrO3), ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and quartz.
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series