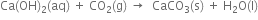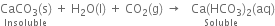Describe briefly the preparation and uses of magnesium chloride (MgCl2.6H2O).
Preparation:
(i) In the laboratory, magnesium chloride is prepared by the action of hydrochloric acid on magnesium oxide or carbonate.

The reaction mixture is cooled and concentrated when crystals of MgCl2.6H2O separate out.
(ii) From carnallite: The mineral carnallite (KCl.MgCl2.6H2O) is powdered and then boiled with water. On cooling KCl is crystallised out while magnesium chloride is left in the mother liquor. The mother liquor is separated, concentrated by evaporation and cooled when crystals of MgCl2.6H2O separate out.
(iii) From sea water: Sea water is concentrated and then treated with lime when magnesium hydroxide gets precipitated.

The precipitate of Mg(OH)2 is dissolved in HCl when a solution of magnesium chloride is obtained. The solution of magnesium chloride on concentration and cooling yields crystals of MgCl2.6H2O.
It is used:
(i) in the preparation of magnesia cement.
(ii) in the extraction of magnesium metal.