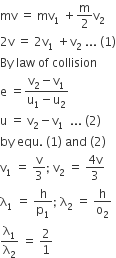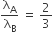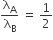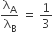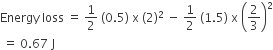A particle A of mass m and initial velocity v collides with a particle B of mass m/2 which is at rest. The collision is head on, and elastic. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelengths λA to λB after the collision is
D.
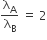

By conservation of linear momentum