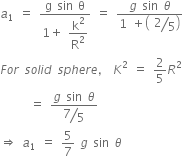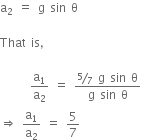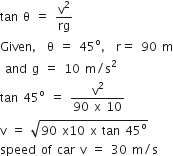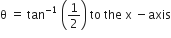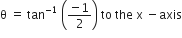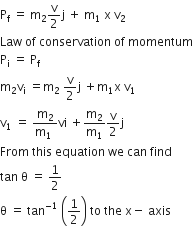A system consists of three masses m1, m2 and m3 connected by a string passing over a pulley P. The mass m1 hangs freely and m2 and m3 are on a rough horizontal table (the coefficient of friction= 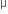 ). the pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The downward acceleration of mass m1 is,
). the pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The downward acceleration of mass m1 is,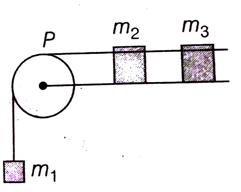
C.
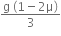
First of all consider the forces on the blocks,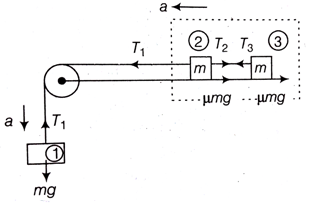
For the 1st block,
mg - T1 = m x a ... (i)
Let us consider second and third block as a system,
Then,
T1 -  = 2m x a
= 2m x a
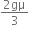
mg ( ) = 3m x a
) = 3m x a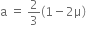



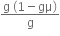
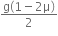



 without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is,
without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is,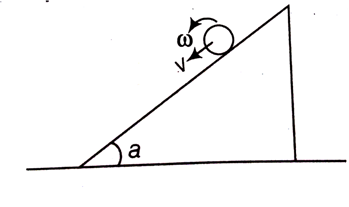 We have in this case,
We have in this case,