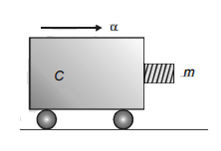
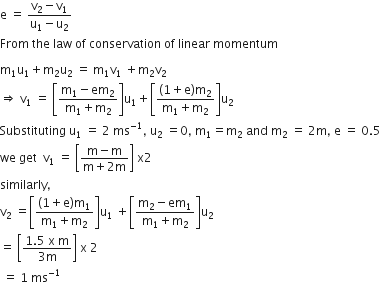
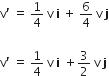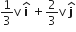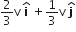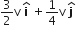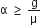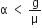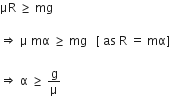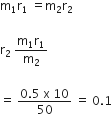A mass m moving horizontally (along the x -axis) with velocity v collides and sticks to mass of 3m moving vertically upward (along the y -axis) with velocity 2v. The final velocity of the combination
A.
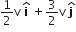
From the law of conservation of linear momentum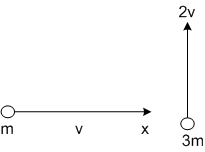
mv + (3m)(2v) = (4m)v'
mv i + 6mv j = 4 mv'