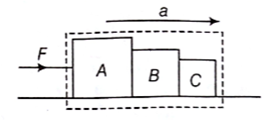
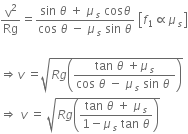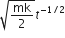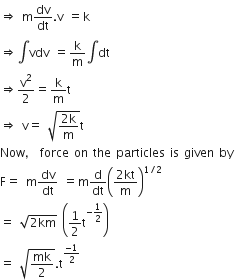It is found that if a neutron suffers an elastic collinear collision with deuterium at rest, fractional loss of its energy is pd; while for its similar collision with carbon nucleus at rest, fractional loss of energy is pc. The values of pd and pc are respectively :
(0,1)
(.89,.28)
(.28,.89)
(0,0)
B.
(.89,.28)
For collision of a neutron with deuterium:
![]()
Applying conservation of momentum:
mv + 0 = mv1 + 2mv2 .....(i)
v2 -v1 = v ...... (ii)
Therefore, Collision is elastic, e = 1
From equ (i) and equ (ii) v1 = -v/3
Now, for the collision of neutron with carbon nucleus

Applying conservation of momentum
mv + 0 = mv1 + 12mv2 ....; (iii)
v = v2-v1 ....(iv)






 . The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is
. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is  . The maximum safe velocity on this road is,
. The maximum safe velocity on this road is,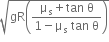
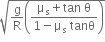
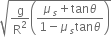
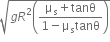
 and the coefficient of friction between the tyres of car and the road is
and the coefficient of friction between the tyres of car and the road is  .
.
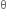 = mg + f1 sin
= mg + f1 sin 
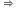 mg = N cos
mg = N cos 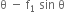 ... (i)
... (i)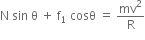 ... (ii)
... (ii)